As the UK navigates the post-pandemic economy with rising inflation and prepares to endure a macro-economic downturn, many organisations are desperate to keep hold of their staff as talent shortages grow in many sectors and hiring freezes are implemented.
Manufacturing Software, ERP, MRP
Manufacturing software systems are important tools for the automation and management of production processes. A wide range of manufacturing companies covering many different vertical sectors rely on manufacturing software to better manage the sourcing and use of material or parts quantities, scheduled production timelines, inventory management and the planning for future order demand. One commonly deployed example of a manufacturing software system is an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution, designed to better manage information concerning orders and materials, finance, Customer Relationship Management etc.over the whole organisation.
8 in 10 UK workers more likely to choose an employer that offers continuous learning and development
Dec 21, 2022

Manufacturers show overwhelming willingness to improve their customer experience, but many face organisational obstacles, according to research from Valtech and Gartner Peer Insights
Dec 21, 2022

Valtech, a global provider of digital services and business transformation, in collaboration with Gartner Peer Insights, has released a global report surveying 100 global manufacturing leaders about the current state of progress in digital transformation and the underlying challenges.
Manufacturing & Logistics IT - December 2022 edition
Dec 19, 2022

In this issue we feature a Special Technology Report looking in depth at the latest developments in the world of Manufacturing Technology.
Also included is a ‘Cover Story’: 10 common mistakes when crafting a cloud strategy, according to Gartner, Inc. and a number of key technology areas in Manufacturing, Printing and Labelling, Supply Chain Management, AIDC/Mobile Computing, Warehouse Management & Security.
Stuck in the dark? Why the energy crisis in manufacturing needs real-time data to keep the lights on and compete
Dec 19, 2022

The ability to predict and adapt to the waves of change will determine the success or failure of manufacturing, writes Alessandro Chimera, Director Digitalisation Strategy, TIBCO.
Late payments stunting growth and crippling cash flow for nearly a third of manufacturing SMEs
Dec 14, 2022

Late payments are putting the brakes on growth and adding to cash flow woes, with over three quarters (77%) of SMEs in the manufacturing sector not being paid on time for the provision of goods and services, according to new research from Growth Lending.
Valmet signs an extension of Chip Quality Agreement with a customer in the Scandinavian region
Dec 13, 2022

Valmet and a customer in the Scandinavian region are continuing their collaboration by signing an extension of the Chip Quality Agreement.
Zebra survey shows eight-in-10 millennials expect more transparency in automotive manufacturing
Dec 12, 2022

Zebra Technologies Corporation has released the findings of its Automotive Ecosystem Vision Study which confirmed automotive manufacturers are under pressure to accommodate growing consumer demands for sustainability and transparency throughout the manufacturing process and fleet managers’ need for the digitisation of operations and supply chain.
Out-of-date technology can waste up to 46% of manufacturers' working days a year
Dec 07, 2022

Technology is often the backbone of many manufacturing businesses, powering growth, efficiency and adaptability. However, internal systems and software can cause many challenges for business owners and employees if not monitored and appropriately reviewed.
Peer Software and SSI Team to increase productivity and data availability for distributed teams in the shipbuilding industry
Dec 06, 2022

At the International WorkBoat Show, Peer Software announced an alliance partnership with SSI, the global software solutions company for the design, engineering, construction and maintenance of shipbuilding projects.
Making sense of coercivity in magnetic materials with machine learning
Dec 06, 2022
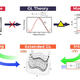
Scientists have developed a meaningful approach to analyse how a material’s microstructure relates to its macroscopic physical properties.
Manufacturing software systems
Manufacturing software systems provide the automation and computational support for complex manufacturing processes. Manufacturing companies leverage manufacturing software systems to carefully manage the timing, types and quantities of materials they purchase in order to ensure that they are able to meet current and future customer demand while at the same time achieving the lowest possible cost and inventory accumulation.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate internal and external management information across an entire organization, embracing finance/accounting, manufacturing, sales and service, customer relationship management, etc. ERP systems facilitate the flow of information between all business functions inside the boundaries of the organisation and manage the connections to outside stakeholders.
Manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) addresses operational planning in units, financial planning, and has a simulation capability to answer "what-if" questions and extension of closed-loop MRP.
CRM or Customer Relationship Management concerns the relationship between an organisation and its customers. The scope of CRM which can vary drastically as it can be used by management, salespeople, people providing service, and even customers could directly access information to find out information.
Cloud computing can be defined as the set of hardware, networks, storage, services, and interfaces that combine to deliver aspects of computing as a service. Cloud services include the delivery of software, infrastructure, and storage over the Internet and is based on user demand. Cloud Computing is the latest stage in the Internet's evolution, providing the means through which everything , from computing power to computing infrastructure, applications, business can be delivered to you as a service wherever and whenever you need.
Cloud computing has some essential characteristics: scalability depending on requirements, offers a way to increase capacity or add capabilities on the fly without investing in new infrastructure, eliminates the need for on-site personnel to maintain computer equipment. No up-front CAPEX (capital expenditure) required, as billing is a pay-as-you-go model, access to the very latest application programming interfaces (APIs).
SaaS (software as a service) is a type of cloud computing delivering a single application through the browser to thousands of customers using a multitenant architecture. On the customer side, it means no upfront investment in servers or software licensing; on the provider side, with just one app to maintain, costs are low compared to conventional hosting. SaaS is emerging to provide service to all aspects of an organisation`s activities in the areas of Manufacturing, ERP, Demand Forecasting, Advanced Planning, S&OP, Supply Chain, Warehousing, Transport Management and HR (human resource).
Business intelligence (BI) is a set of theories, processes and technologies that convert raw data into useful information for business purposes. BI can handle large amounts of information to help identify and develop new opportunities to gain market advantage over competitors. The amounts of data that are now being gathered as a result of because they are increasingly being gathered by a growing range of diverse and ubiquitous information-gathering devices.
These data sets become so large and complex that it becomes difficult to process using on-hand database management tools or traditional data processing applications. The trend to larger data sets is due to the additional information derivable from analysis of a single large set of related data, as compared to separate smaller sets with the same total amount of data. The current challenges of BIG DATA include the capture, storage, search and share capability, transfer, analysis, and visualisation. Every day, we create 2.5 quintillion bytes of data — so much that 90% of the data in the world today has been created in the last two years alone. This data comes from everywhere: sensors used to gather climate information, posts to social media sites, digital pictures and videos, purchase transaction records, and cell phone GPS signals to name a few. This data is big data.
It is estimated that the world's technological per-capita capacity to store information has roughly doubled every 40 months since the 1980s. The challenge for large enterprises is determining who should own big data initiatives that straddle the entire organisation and how this data can be used as a source of revenue and to gain competitive advantage.
