Suprema AI, provider of artificial intelligence–based integrated security solutions, launched a high-performance face recognition OEM module called ‘Q-Face Pro’ at ISC West, the largest security exhibition in North America.
Automatic Identification/Datacapture, AIDC, RFID
Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC) refers to the process of automatically identifying and collecting data about objects/goods, then logging this information in a computer. The term AIDC refers to a range of different types of data capture devices. These include barcodes, biometrics, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), magnetic stripes, smart cards, OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and voice recognition. AIDC devices are deployed in a wide range of environments, including: retail, warehousing, distribution & logistics and field service. The first RFID solutions were developed in 1980s. It has since been deployed in a range of markets including Automated Vehicle Identification (AVI) systems due to RFID's ability to track moving objects. RFID is also effective in challenging manufacturing environments where barcode labels might not prove resilient enough.
Smartphone designer Alain Capo honoured for contribution to literacy
Apr 03, 2023

West African innovator and technology-telecommunications company owner Alain Capo has been announced the winner of the World Literacy Award for his outstanding contribution in the individual category.
The risk of breaking electronic devices rises 24% over Easter, new data reveals
Apr 03, 2023

New data has revealed that there’s a 24% rise in Brits dealing with broken laptops, tablets and phones over the Easter break each year, making it the riskiest holiday for devices.
The Growing Importance of Asset Tracking and Management in Business Operations
Mar 30, 2023

By Fraser Spence, freelance writer.
Discover the latest trends and innovations in the asset tracking and management industry, and how it can help businesses achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and profitability.
The Security Tech Future-Proofing Freight Forwarding Warehouses
Mar 22, 2023

By James Cavendish, freelance writer.
Thanks to technological advancements, freight forwarding warehouses can now take advantage of various highly effective security technologies. These allow them to minimize risks such as workers' injuries, vandalism, theft, and fires.
KnowBe4 launches phishing security resource kit to help combat the most common form of social engineering
Mar 20, 2023

KnowBe4 has released its phishing security resource kit to help end users defend themselves and their organisations against the threat of phishing attacks.
Sealey Tools achieves significant productivity uplift with new voice-enabled solution from Dakota
Mar 15, 2023

Founded in 1978, Sealey Tools is well-known nationally and internationally as a leading brand of professional tools and workshop equipment. When the company experienced an unexpected, significant and sustained increase in orders during the Covid pandemic lockdown, its warehouse was under extreme pressure to keep up with such an unprecedented upturn in demand.
Hornetsecurity launches VM Backup V9 to challenge ransomware attacks
Mar 15, 2023

Global cybersecurity provider Hornetsecurity has launched VM Backup V9 – the newest version of its award-winning virtual machine (VM) backup, replication and recovery solution.
Getting started with automation
Mar 15, 2023

Retail logistics automation has never been more important. In a tough economic market, slow and inaccurate picking can wipe out margin, especially when errors contribute to expensive returns.
Staff shortages are adding to inefficiency and workplace stress, making it vital to create a more attractive working environment, preferably one that minimises heavy lifting and enables staff to be quickly productive.
Demand for cash automation technology rises as retailers seek efficiency and security
Mar 08, 2023
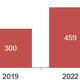
Investment in devices deployed both in the back office and at the point of sale is increasing, with more than 900,000 units installed globally at end-2022.
Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC)
Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC) refers to the methods of automatically identifying objects, collecting data about them, and entering that data directly into computer systems (i.e. without human involvement). Technologies typically considered as part of AIDC include bar codes, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), biometrics, magnetic stripes, Optical Character Recognition (OCR), smart cards, and voice recognition. AIDC is also commonly referred to as “Automatic Identification,” “Auto-ID,” and "Automatic Data Capture."
Barcoding has become established in several industries as an inexpensive and reliable automatic identification technology that can overcome human error in capturing and validating information. AIDC is the process or means of obtaining external data, particularly through analysis of images, sounds or videos. To capture data, a transducer is employed which converts the actual image or a sound into a digital file which can be later analysed. Radio frequency identification (RFID) is relatively a new AIDC technology which was first developed in 1980’s. The technology acts as a base in automated data collection, identification and analysis systems worldwide
In the decades since its creation, barcoding has become highly standardised, resulting in lower costs and greater accessibility. Indeed, word processors now can produce barcodes, and many inexpensive printers print barcodes on labels. Most current barcode scanners can read between 12 and 15 symbols and all their variants without requiring configuration or programming. For specific scans the readers can be pre-programmed easily from the user manual.
Despite these significant developments, the adoption of barcoding has been slower in the healthcare sector than the retail and manufacturing sectors. Barcoding can capture and prevent errors during medication administration and is now finding its way from the bedside into support operations within the hospital.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is the wireless non-contact use of radio-frequency electromagnetic fields to transfer data. Unlike a bar code, the tag does not necessarily need to be within line of sight of the reader, and may be embedded in the tracked object. It can also be read only or read-write enabling information to be either permanently stored in the tag or it can be read-write where information can be continually updated and over-written on the tag.
RFID has found its importance in a wide range of markets including livestock identification and Automated Vehicle Identification (AVI) systems and are now commonly used in tracking consumer products worldwide. Many manufacturers use the tags to track the location of each product they make from the time it's made until it's pulled off the shelf and tossed in a shopping cart. These automated wireless AIDC systems are effective in manufacturing environments where barcode labels could not survive. They can be used in pharmaceutical to track consignments, they can also be used in cold chain distribution to monitor temperature fluctuations. This is particularly useful to ensure frozen and chilled foods have not deviated from the required temperature parameters during transit.
Cost used to be a prohibitive factor in the widespread use of RFID tags however the unit costs have reduced considerably to make this a viable technology to improve track and trace throughout the supply chain. Many leading supermarket chains employ RFID insisting that their suppliers incorporate this technology into the packaging of the products in order to improve supply chain efficiency and traceability.

